 Japanese
Japanese English
English Korea
Korea Japanese
Japanese English
English Korea
KoreaMachu Picchu is a ruin of the ancient Inca Empire located on a ridge at an altitude of about 2,450 m in the Andes Mountains of Peru, South America. Since the existence of the ruins cannot be confirmed from the foot of the mountain, it is called "aerial city" or "city with lost inca". In addition to being a World Heritage Site, it was selected as one of the New Seven Wonders of the World in July 2007. The ruins consist of a temple and a residential area, and terraced fields spread out on the slope of about half of the total area. The masonry of the building is so precisely assembled that even the razor blade does not pass through the gap, and even after hundreds of years, the figure remains firmly. Why was a fortified city built on such a high-altitude cliff? There is a theory that it was a city that the Inca Empire once built to protect treasures from the invasion of Spain, and that it was the last fort, but the reason is not clear because the Andean civilization has no letters. It is said that the Inca people lived in this secret city for about 80 years and then moved further into the interior, leaving Machu Picchu, where advanced civilization flourished. It hasn't been seen by humans for hundreds of years since then, and became known to the world on July 24, 1911, with the discovery of American explorer Hiram Bingham.
マチュピチュは、南米ペルーのアンデス山脈の標高約2,450mの尾根にある古代インカ帝国の遺跡です。 山麓からは遺跡の存在が確認できないことから、「空中都市」または「インカ帝国を失った都市」と呼ばれています。 世界遺産に加え、2007年7月には世界の七不思議のひとつに選ばれました。遺跡は寺院と住宅地で構成され、約半分の斜面に段々畑が広がっています。 総面積。 建物の石積みは非常に精密に組み立てられているため、かみそりの刃でさえ隙間を通り抜けることはなく、数百年経ってもその姿はしっかりと残っています。 なぜこのような標高の高い崖の上に要塞都市が建てられたのでしょうか。 かつてインカ帝国がスペインの侵略から財宝を守るために建てた都市であり、最後の砦だったという説がありますが、アンデス文明には文字がないため理由は不明です。 インカの人々はこの秘密の街に約80年間住んでいた後、さらに奥地に移り、高度な文明が栄えたマチュピチュを離れたと言われています。 それ以来何百年もの間人間に見られず、1911年7月24日にアメリカの探検家ハイラムビンガムの発見で世界に知られるようになりました。
마추 픽추는 남미 페루의 안데스 산맥에서 고도 약 2,450m의 산등성이에 위치한 고대 잉카 제국의 폐허입니다. 산기슭에서는 폐허의 존재를 확인할 수 없기 때문에 '공중 도시'또는 '잉카를 잃어버린 도시'라고 불린다. 세계 유산에 등재되어 2007 년 7 월 세계 7 대 불가사의 중 하나로 선정되었습니다. 유적은 사찰과 주거 지역으로 구성되어 있으며, 약 절반의 경사면에 계단식 들판이 펼쳐져 있습니다. 전체 면적. 건물의 벽돌은 매우 정밀하게 조립되어 면도날조차도 틈새를 통과하지 못하며 수백 년이 지난 후에도 그 모습은 단단히 유지됩니다. 왜 그렇게 높은 절벽 위에 요새화 된 도시가 세워졌습니까? 잉카 제국이 한때 스페인 침략으로부터 보물을 지키기 위해 지은 도시 였고 마지막 요새 였다는 이론이 있지만 안데스 문명에는 글자가 없기 때문에 그 이유는 분명하지 않습니다. 잉카인들은이 비밀의 도시에서 약 80 년 동안 살다가 내부로 더 이동하여 선진 문명이 번성했던 마추 픽추를 떠났다고합니다. 그 이후로 수백 년 동안 인간은 본 적이 없었으며 1911 년 7 월 24 일 미국 탐험가 Hiram Bingham의 발견과 함께 세계에 알려졌습니다.
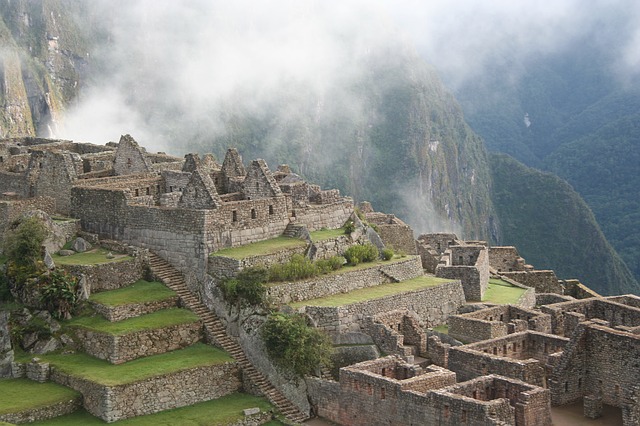




Machu Picchu was built in the 15th century. He slept for nearly 400 years at one of the ruins of the fallen Inca Empire, but was discovered in 1911 by American university professor Hiram Bingham. The Inca people deliberately built cities on the highlands of the Andes, on narrow mountain ridges. The ruins, which cover a total area of 5 km, have almost complete traces of temples, houses, terraced fields and irrigation facilities, and people can feel their lives. But why was the fortified city created in the highlands, which are not easy to live in? There are various theories as to the reason, but it has not been clarified yet.
マチュピチュは15世紀に建てられました。 彼は倒れたインカ帝国の廃墟の1つで400年近く眠りましたが、1911年にアメリカの大学教授ハイラムビンガムによって発見されました。 インカの人々は、アンデスの高地、狭い山の尾根に故意に都市を建設しました。 総面積5kmの遺跡には、寺院、家屋、棚田、灌漑施設がほぼ完全に残っており、人々は自分たちの生活を感じることができます。 しかし、なぜ住みにくい高地に要塞都市ができたのでしょうか。 その理由については様々な説がありますが、まだ解明されていません。
마추피추는 15 세기에 지어졌습니다. 그는 쓰러진 잉카 제국의 유적 중 하나 400 년 가까이 잠했지만, 1911 년에 미국의 대학 교수 하이 럼 빙엄에 의해 발견되었습니다. 잉카 사람들은 안데스 산맥의 고원 좁은 산등성이에 고의로 도시를 건설했습니다. 총 면적 5km의 유적은 사원, 가옥, 계단식 논 관개 시설이 거의 완전하게 남아 있으며, 사람들은 자신의 삶을 느낄 수 있습니다. 그런데 왜 살기 어려운 고지에 요새 도시가 생긴 것입니까? 그 이유에 대해서는 다양한 설이 있지만, 아직 해명되어 있지 않습니다.
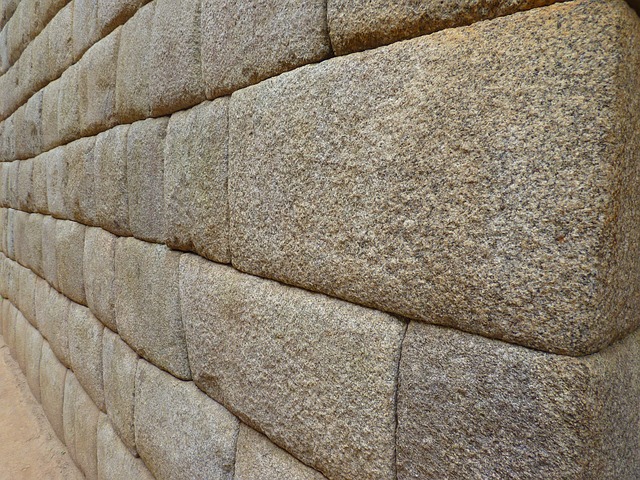

Since the Inca Empire did not have letters, its history is still shrouded in many mysteries. Inheriting the ancient Andean civilization, a unique culture such as metal engraving, textiles, and earthenware flourished. Among them, stone processing and construction techniques are characteristic, and in Cusco, the capital of the Inca Empire, palaces and temples were built on the foundation of elaborate stone walls. There are no gaps between the stones in the stone wall, and they are in close contact with each other with an accuracy that does not allow a razor to pass through. However, many buildings of the Inca era were destroyed at the end of the empire during the 16th century Spanish invasion. Machu Picchu was built on a ridge above 2,400 m above sea level, so it escaped invasion and conveys the high level of masonry technology.
インカ帝国には手紙がなかったので、その歴史はまだ多くの謎に包まれています。 古代アンデス文明を受け継いで、金属彫刻、織物、陶器などの独特の文化が栄えました。 その中でも石の加工や工法が特徴的で、インカ帝国の首都クスコでは、精巧な石垣を土台に宮殿や寺院が建てられました。 石壁の石の間に隙間はなく、かみそりが通過できない精度で互いに密着しています。 しかし、インカ時代の多くの建物は、16世紀のスペインの侵略の間に帝国の終わりに破壊されました。 マチュピチュは海抜2,400mの尾根に建てられたため、侵入を免れ、高度な組積造技術を伝えています。
잉카 제국은 편지가 없었기 때문에, 그 역사는 아직도 많은 수수께끼에 싸여 있습니다. 고대 안데스 문명을 이어 금속 조각, 직물, 도자기 등의 독특한 문화가 번창했습니다. 그 중에서도 돌의 가공 및 공법이 특징으로, 잉카 제국의 수도 쿠스코에서 정교한 돌담을 바탕으로 궁전과 사원이 세워졌습니다. 석벽의 돌 사이에 틈새가 아니라 면도기가 통과 할 수없는 정밀도로 서로 밀착하고 있습니다. 그러나 잉카 시대의 많은 건물은 16 세기 스페인의 침략 동안 제국의 끝에 파괴되었습니다. 마추피추는 해발 2,400m의 능선에 지어진 때문에 침입을 면치 고급 벽돌 기술을 전하고 있습니다.

The waterway of Machu Picchu was made of stone, and abundant water was flowing there. But how did you get the water on a steep mountain without using a pump? In fact, the area around Machu Picchu was blessed with a lot of rain and water. Therefore, there was spring water in the forest a little away from the ruins, and we were able to secure a water source. The waterways are carefully calculated so that the water pumped from the mountains goes down the slopes and supplies water to various fields and residential areas. Rice terraces built along the slopes of the mountains used the water provided to grow potatoes and corn. There are also 16 daily and ceremonial water stations where you can see the excellent water use techniques of the Inca people. It is said that Machu Picchu lived for about 100 years, but even after 500 years, the waterways continue to function and supply water.
マチュピチュの水路は石でできていて、そこには豊富な水が流れていました。 しかし、ポンプを使わずに急な山でどうやって水を汲んだのでしょうか? 実際、マチュピチュ周辺はたくさんの雨と水に恵まれていました。 そのため、廃墟から少し離れた森に湧き水があり、水源を確保することができました。 山から汲み上げた水が斜面を下って、さまざまな畑や住宅地に水を供給するように、水路は慎重に計算されています。 山の斜面に沿って作られた棚田では、供給された水を使ってジャガイモとトウモロコシが栽培されました。 また、16の日常生活や儀式用の給水所があり、インカの人々の優れた水利用技術を見ることができます。 マチュピチュには約100年住んでいたと言われていますが、500年経っても水路は機能し続け、水を供給しています。
마추피추 수로는 돌로되어 있고, 거기에는 풍부한 물이 흐르고있었습니다. 그러나 펌프를 사용하지 않고 가파른 산에서 어떻게 물을 뜬 것일까 요? 실제로 마추피추 주변에는 많은 비와 물이 풍부했습니다. 따라서 폐허에서 조금 떨어진 숲에 샘물이 수원을 확보 할 수있었습니다. 산에서 퍼 올린 물이 사면을 내려 다양한 밭이나 주거 지역에 물을 공급하도록 수로는 신중하게 계산되고 있습니다. 산의 경사면을 따라 만들어진 계단식으로 공급 된 물을 사용하여 감자와 옥수수가 재배되었습니다. 또한 16의 일상 생활과 의식의 급 수소가 잉카 사람들의 뛰어난 물 이용 기술을 볼 수 있습니다. 마추피추에는 약 100 년 살았던 것으로 알려져 있습니다 만, 500 년이 지나도 수로는 계속 작동 물을 공급하고 있습니다.
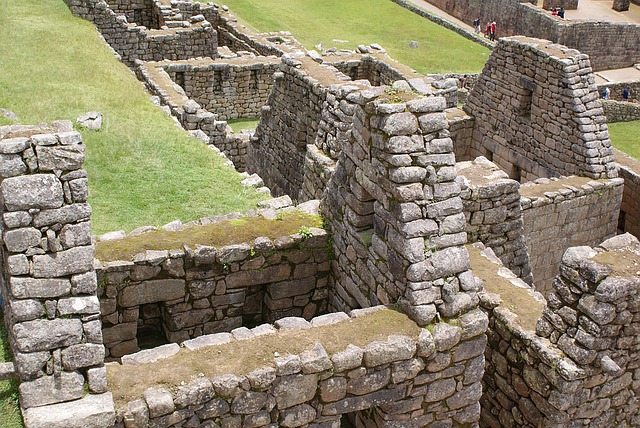

What many scholars are currently advocating is Machu Picchu's residence depends on the status of the resident human It is the theory that it was divided.
現在多くの学者が提唱しているのは、マチュピチュの住居は住人のフマの地位に依存しているということです。それは分割されたという理論です。
현재 많은 학자들이 제창하고있는 것은 마추피추 집은 거주자의 부마의 지위에 의존하고 있다는 것입니다. 그것은 분할되었다는 이론입니다.
There are subtle differences in the theories, The general theory is that the living quarters were divided into four. High-ranking people such as priests and royalty, Engineer (or researcher), And there are four areas of farmers (commoners).
理論には微妙な違いがあります。一般的な理論では、居住区は4つに分割されています。 僧侶や王族、技術者(または研究者)などの高位の人々、そして農民(庶民)の4つの分野があります。
이론에는 미묘한 차이가 있습니다. 일반적인 이론은 거주 구역은 4 개로 분할되어 있습니다. 승려 나 왕족 기술자 (또는 연구자) 등 고위 사람들, 그리고 농민 (서민)의 4 가지 영역이 있습니다.
In the capital city of the Inaka country, I am able to re-create it. It's a good thing, but it's not good for me. It's not good for me. It's good for me. It's lined up. It wasn't there. It wasn't there. It wasn't there. It's a good idea.
インカ帝国の都市に見られる見事な石の建造物のほとんどは、漆喰を使わずに建てられた。石は計算したように正確に切り出され、隙間なく積み上げられている。その建築様式には、見た目の美しさだけでなく、工学的な利点もある。ペルーは地質活動が活発な国で、首都のリマやクスコも地震に見舞われたことがある。マチュピチュの下にも、2本の断層線が通っている。地震が起こると、インカの建物は「踊り出す」と言われている。つまり、地震の揺れに伴って石が互いに衝突しあい、最終的に元の位置に納まる。このような建て方でなければ、マチュピチュの多くの有名な建造物はとうの昔に崩落していただろう。
잉카 제국의 도시에서 볼 수있는 멋진 돌 건물의 대부분은 석고를 사용하지 않고 지어졌다. 돌은 계산 된대로 정확하게 잘라내어 빈틈없이 쌓여있다. 그 건축 양식은 외형의 아름다움뿐만 아니라 공학적인 이점도있다. 페루는 지질 활동이 활발한 국가로, 수도 리마와 쿠스코도 지진에 휩쓸린 수있다. 마추피추 아래에 2 개의 단층 선이 다니고있다. 지진이 발생하면 잉카의 건물은 "춤추 기"라고되어있다. 즉, 지진의 흔들림에 따라 돌이 서로 충돌하고 서로 결국 제자리로 들어갈. 이러한 건축 방법 않으면, 마추피추의 많은 유명한 건물은 오래전에 붕괴하고 있었을 것이다.
The reason is the very good masonry technology of the Inca era. Peruvian guidebooks often say, "Inca masonry is so accurate that a single razor blade cannot pass through," but this is by no means an exaggeration. If all the stones have the same shape, it's no wonder that there are no gaps, but when you see the disjointed stones combined like a complex puzzle, no matter how you look at it, the stones melt and mold I think it's made just by putting it in.
その理由は、インカ時代の非常に優れた組積造技術です。 ペルーのガイドブックには、「1枚のかみそりの刃が通過できないほど正確なインカの石積み」とよく書かれていますが、これは決して誇張ではありません。 すべての石が同じ形であれば、隙間がないのも不思議ではありませんが、ばらばらの石が複雑なパズルのように組み合わされているのを見ると、どのように見ても石を溶かして型に入れるだけで作られているとしか思えません。
그 이유는 잉카 시대의 뛰어난 벽돌 기술입니다. 페루의 가이드 북에는 "1 개의 면도날이 통과 할 수 없을 정도로 정확한 잉카의 벽돌"잘 쓰여져 있습니다 만, 이것은 결코 과장이 아닙니다. 모든 돌 같은 모양이면 틈이없는 것도 놀라운 일이 아니지만, 붕괴 돌이 복잡한 퍼즐처럼 조합되어있는 것을 보면 어떻게 봐도 돌을 녹여 형식 에 넣는 것만으로 만들어져 있다고 밖에 생각되지 않습니다.
Peru, which is located in the Pacific Rim, is an earthquake-prone country like Japan, but it is strong against earthquakes as well as solid Inca stonework. The European-style building that the Spaniards put on top of it will be destroyed by every major earthquake, no matter how many times it is rebuilt, but the Inca stonework below will never collapse. So even now, there are many private houses in Peru that use it as a wall or a base for their homes.
環太平洋に位置するペルーは、日本のように地震が発生しやすい国ですが、地震に強く、インカの石細工もしっかりしています。 スペイン人がその上に置いたヨーロッパ風の建物は、何度再建されても大地震のたびに破壊されますが、下のインカの石細工は決して崩壊しません。 そのため、現在でもペルーには、家の壁や土台として使用している民家がたくさんあります。
태평양에 위치한 페루는 일본과 같이 지진이 발생하기 쉬운 나라입니다 만, 지진에 강하고, 잉카의 석조도 확실히하고 있습니다. 스페인 사람이 그 위에 올려 유럽풍의 건물은 여러 번 재건도 대지진 때마다 파괴되지만, 아래의 잉카의 석조 결코 붕괴하지 않습니다. 따라서 지금도 페루는 집의 벽이나 바탕으로 사용하는 민가가 많이 있습니다.